Below is a barebones overview of the evolution of plants, based on notes from a module in the University of Copenhagen's Origins: Formation of the Universe, Solar System, Earth and Life. For additional information, check here and here.
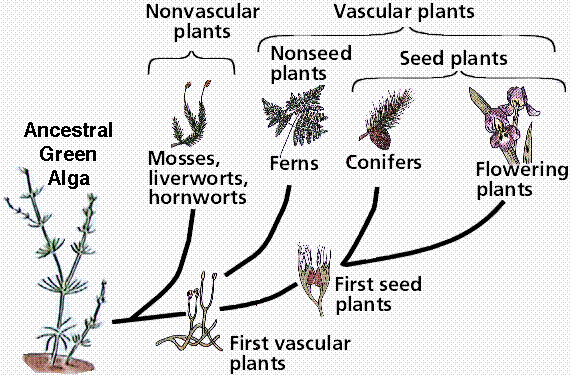
Image credit: M. J. Farabee
Features of plants
- Ordovician (450 Mya): plants evolved from green algae living continental freshwater ponds
- Harsh environmental conditions on land drove the evolution of land plants
- Limited water
- Reproduction
- Spores: coated male gametes protect against dessication and strong UV light
- Oldest spore discovered: 450 million years old, deposited in marine sediments after rivers transported it from the land to the sea
- Seeds: appeared in the late Devonian; parent provides egg cell with protection and nutrients
- Spores: coated male gametes protect against dessication and strong UV light
- Roots and vascular systems: allow plants tap deeper water supplies and transport water and nutrients
- First vascular plant fossils found from the early Devonian (420 Mya)
- Simple, forked branches with spores at tip; lacked leaves (entire plant was photosynthetic); inhabited moist areas
- First vascular plant fossils found from the early Devonian (420 Mya)
- Cuticle: waxy outer layer minimizes evaporative water loss
- Require stomata, breathing holes, to allow uptake of carbon dioxide
- Require stomata, breathing holes, to allow uptake of carbon dioxide
- Reproduction
- Gravity
- Lignin: rigid material in plant cell walls that allows plant stems to stand upright, which facilitates capture of sunlight
- Roots also help support plants
- Limited water
Major vascular plant groups
- Spore plants
- Lycophytes (club mosses)
- Appeared in the early Devonian
- Small herbaceous plants and oldest extant vascular plants
- Devonian Sigillaria reached 45 m tall and formed vast swamp forests
- Ferns
- Appeared in late Devonian
- Developed large lobed leaves to capture sunlight
- Ranged in size from small ephiphytic (lives on other plants) plants to large trees
- Exploited understorey habitats
- Lycophytes (club mosses)
- Seed plants
- Gymnosperms
- Conifers
- Seeds in cones
- Wind-pollinated
- Wollemia: modern plant with pollen from the Cretaceous
- Cycads
- Woody, barrel-shaped trunk with crown of large, stiff, evergreen leaves
- Common in the Jurassic; three families alive today
- Gingkos
- Fan-like leaves with numerous non-crossing parallel veins
- Widespread during the Jurassic; one species (found in China) alive today
- Conifers
- Angiosperms: flowering plants
- Largest plant group in modern times
- Oldest fossil pollen from the Cretaceous (136 Mya)
- Petals and sepals developed from leaves
- Rely on insects, birds, bats for pollination
- Seeds enclosed in carpels
- Gymnosperms






